Organic farming systems are agricultural methods that prioritize sustainability, biodiversity, and the use of natural processes. These systems avoid synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), focusing instead on organic fertilizers, crop rotation, and biological pest control. The aim is to enhance soil fertility, promote ecological balance, and conserve biodiversity.
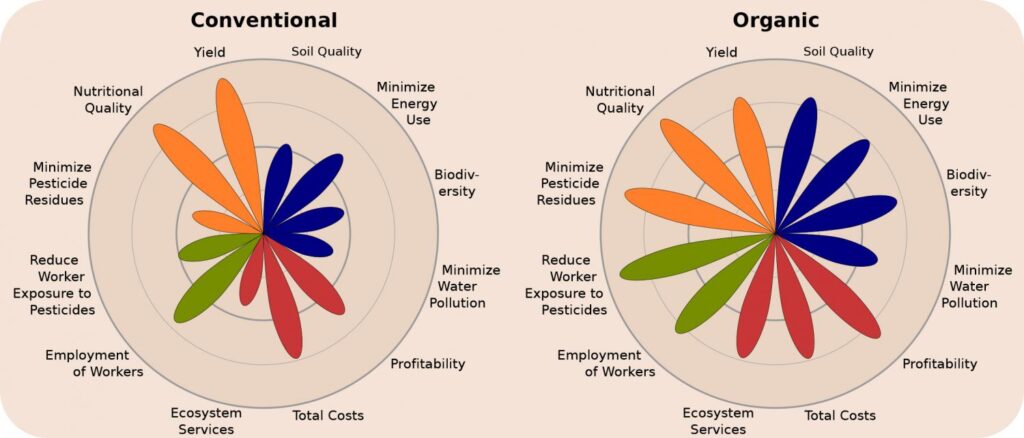
Comparison of Conventional and Organic Farming Systems
This image provides a comparative analysis of conventional and organic farming systems across various metrics such as yield, soil quality, biodiversity, and pesticide use. It visually highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each system, showcasing how organic farming excels in areas like soil health and minimizing environmental impact, while conventional farming often achieves higher yield and profitability. This comparison aids in understanding the trade-offs between these two agricultural approaches.
Key Principles of Organic Farming Systems:
- Soil Health: Organic farming emphasizes the use of natural compost, green manure, and crop residues to enhance soil structure and fertility. Techniques like crop rotation and intercropping help maintain soil health by preventing nutrient depletion.
- Biodiversity: Organic farms promote a diverse ecosystem by growing a variety of crops and maintaining natural habitats. This diversity helps control pests and diseases naturally, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
- Pest Management: Biological pest control methods, such as using beneficial insects and plants that repel pests, are integral to organic farming. Natural predators are encouraged to keep pest populations in check.
- Animal Welfare: In organic livestock farming, animals are raised in natural conditions with access to outdoor spaces and organic feed. This approach ensures high welfare standards and reduces the use of antibiotics and growth hormones.
- Sustainability: Organic farming systems aim to reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. This includes minimizing soil erosion, conserving water, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions through sustainable practices.
Benefits of Organic Farming Systems:
- Environmental Protection: By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic farming reduces pollution and protects water quality.
- Healthy Food: Organic produce is free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, often perceived as healthier by consumers.
- Economic Viability: Organic products typically fetch higher market prices, providing economic benefits to farmers.
Mandako’s Role in Organic Farming:
Mandako supports organic farming systems with equipment designed to enhance soil health and efficiency. For instance, Mandako Land Rollers can help prepare seedbeds and manage crop residues, crucial for maintaining soil structure in organic farming. Additionally, Mandako Vertical Tillage Machines are ideal for residue management and promoting soil aeration, essential for organic crop production.
